Rethinking Device Destruction for Data Security and Sustainability
As sustainability and social responsibility move to the top of corporate agendas, IT asset disposition (ITAD) is getting fresh scrutiny. A 2025 report by Blancco Technology Group reveals a critical but often overlooked risk in data management: more data loss incidents are caused by stolen devices than ransomware or stolen credentials. In response, many companies destroy perfectly functional computers and hardware, but this “shred first” approach often leads to unnecessary e-waste and lost opportunities for refurbishment.
How Common Is Unnecessary Device Destruction?
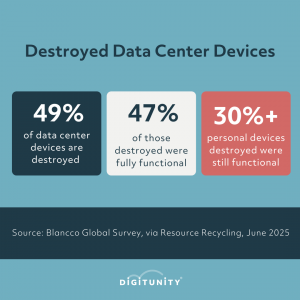
According to Blancco’s global survey, 49% of devices from data centers are destroyed for privacy reasons. Of those destroyed devices, 47% were still functional. Personal devices like smartphones, tablets and computers were unnecessarily destroyed less often, but still over 30% were functional when destroyed. That’s millions of usable computers lost each year, even as more than 1 in 7 households in the United States lack a home computer.
Why Do Companies Destroy Devices Instead of Reusing Them?
The primary reason is fear of sensitive data leaks. Many organizations believe physical destruction is the only way to be sure data cannot be recovered. However, this isn’t always required, and it carries steep financial, environmental, and social costs, especially for those working to increase digital access in communities.
Is Data Destruction the Only Way to Stay Secure?
No. Today, certified data erasure using approved software offers a secure alternative. Standards such as IEEE 2883 and NIST SP 800-88 show that software-based data sanitization is as effective as shredding or crushing devices, while also allowing these devices to be safely reused or donated. Certified data erasure ensures that all data is unrecoverable, creating a verified audit trail for compliance purposes.
However, validation is critical in situations where devices are physically damaged or BIOS-locked, and software erasure may fail to work. In highly regulated industries like defense, finance, or healthcare, physical destruction of the hard drives may still be required to meet strict security and compliance rules.
Chain of custody is another important factor. Data security risks can arise after a device leaves your facility, during transportation, or before it is wiped by a partner. Remote and automated erasure solutions can help address this risk by ensuring devices are wiped before leaving a site.
While certified data erasure is sufficient for most scenarios, best practices require validation, attention to device condition, and careful management of the chain of custody, especially for sensitive data and regulated environments.
What are the Risks and Benefits of Device Reuse?
Risks:
The Blancco report found that 17% of organizations experienced data leaks from devices that were not properly wiped before reuse. This gap can be closed by adhering to certified data wiping standards and implementing robust device management policies.
Benefits:
Securely reusing computers
- Reduces e-waste and landfill burden
- Lowers total IT costs
- Expands access to technology for underserved communities
- Supports sustainability goals and ESG compliance
How Does Device Donation Support ESG and Community Goals?
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) Alignment:
- Environmental: Reduces e-waste and the carbon footprint associated with the production of new devices.
- Social: Expands the reach of digital opportunity by placing computers into the hands of those who need them, not just providing access in public spaces.
- Governance: Meets increasing compliance demands around privacy, reporting, and asset tracking.
- Community Impact: Organizations that make device donation a standard practice help strengthen workforce readiness, support student learning, and improve access to healthcare in the communities they serve. Read how H&R Block is driving both social impact and corporate responsibility with their retired technology.
What Is the Best Practice for Secure, Sustainable IT Asset Disposition?
Key steps:
- Use certified data erasure software to sanitize data on end-of-life devices.
- Prioritize reuse and donation over destruction whenever possible.
- Involve IT, compliance, and sustainability leaders in device disposition policies.
- Stay current with the latest standards (IEEE 2883, NIST SP 800-88) to align security and ESG goals.
- Track devices throughout their lifecycle for transparency and accountability.
How Can Organizations Reduce E-Waste While Protecting Data?
- Replace “shred only” policies with data erasure and responsible reuse practices.
- Partner with nonprofits like Digitunity to donate computers securely and make ownership possible for more people.
- Educate teams on new compliance, sustainability, and data management standards.
- Monitor for changes in technology, AI, and privacy regulations that affect device disposition.
Why Move Beyond Computer Access Toward Computer Ownership?
Access means someone might occasionally use a public or shared device. Ownership means a student, job seeker, or family member has their own computer, free to use for learning, job applications, healthcare, and more, whenever they need it.
Destroying usable computers is a missed opportunity for millions of people to pursue education, build economic stability, access healthcare, and participate more fully in civic life.
Moving from destruction to donation is a strategy that reduces e-waste, advances ESG goals, and changes lives. Secure, structured donations make computer ownership possible and multiply the positive impact on your community.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is destroying old computers necessary for data security?
No, physical destruction is not the only way to keep data safe. Certified data erasure, when performed using recognized standards, fully removes all data from devices, making them safe for reuse or donation without compromising security.
What is certified data erasure and how does it work?
Certified data erasure is a process that permanently removes all data from a device using specialized software, in compliance with industry standards such as NIST SP 800-88 and IEEE 2883. It provides an audit trail and proof of sanitization, ensuring data cannot be recovered.
How can organizations reduce e-waste from IT assets?
Organizations can reduce e-waste by incorporating certified data erasure into their IT asset disposition process, prioritizing device donation or reuse over destruction, and partnering with trusted facilitators to manage secure, responsible redistribution.
Can you safely donate used computers from a business?
Yes, if devices are properly wiped using certified data erasure standards, they can be securely donated to benefit others.
Related resources:
Digitunity is a national nonprofit organization with a mission to make owning a computer possible for everyone. Engaged in advancing digital opportunity for nearly forty years, Digitunity generates and places donated computers with organizations serving people in need, supports a national practitioner network, and advises states, cities, and coalitions on strategies to meet the ongoing device needs of people impacted by the digital divide.